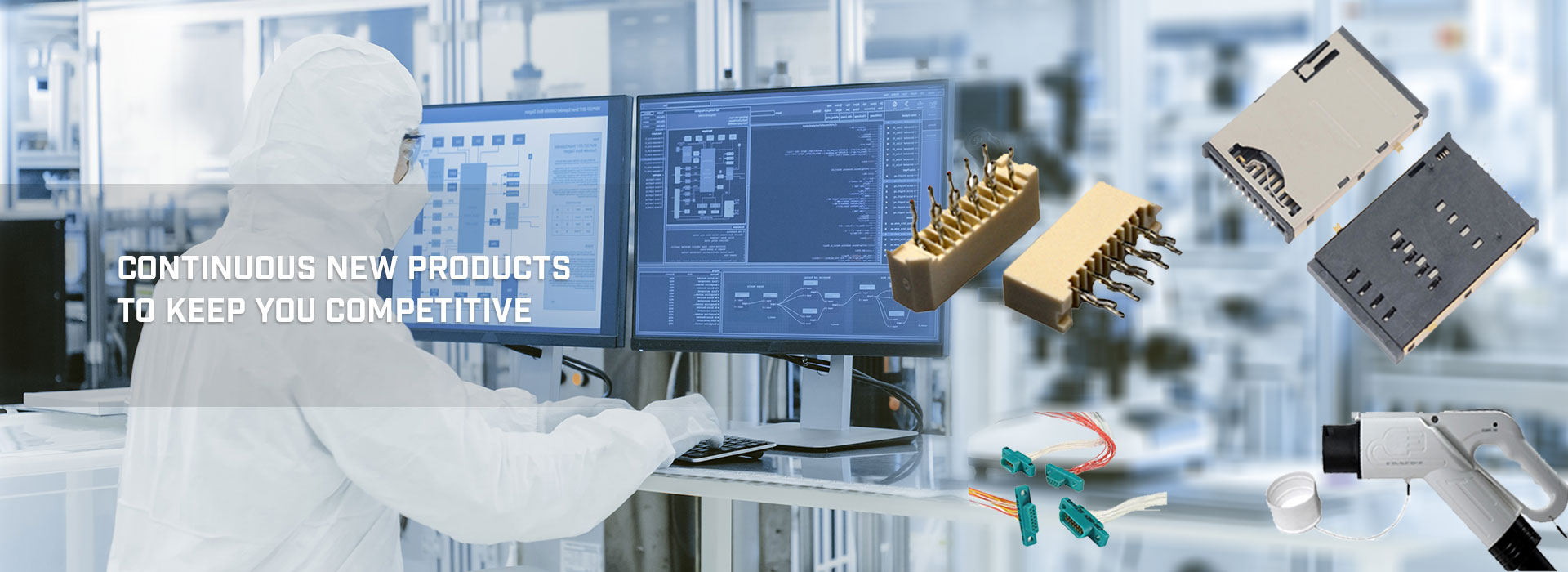
What is a relay?
Relay is an electrical control device, which makes the controlled quantity change in a predetermined step in the electrical output circuit when the change of input quantity (excitation quantity) meets the specified requirements. It has the interactive relationship between the control system (also known as input loop) and the controlled system (also known as output loop). Usually used in automatic control circuit, it is actually an "automatic switch" that uses small current to control high current operation. Therefore, it plays the role of automatic regulation, safety protection, conversion circuit and so on.
Relay classification:
1. Classified according to the working principle or structural characteristics of the relay:
1) Electromagnetic relay: an electrical relay that works by using the suction force generated by the current in the input circuit between the electromagnet core and the armature.
2) Solid state relay: it refers to a relay with input and output isolation in which electronic components perform their functions without mechanical moving components.
3) Temperature relay: a relay that acts when the external temperature reaches a given value.
4) Reed relay: it is a relay that opens, closes or converts lines by using the reed action sealed in the tube and having the dual functions of electric shock reed and armature magnetic circuit.
5) Time relay: when the input signal is added or removed, the output part needs to delay or limit the time until the specified time to close or disconnect its controlled line relay.
6) High frequency relay: a relay with minimum loss for switching high frequency and RF lines.
7) Polarization relay: it is a relay operated by the combined action of polarization magnetic field and control current through the magnetic field generated by the control coil. The action direction of the relay depends on the direction of the current flowing through the control coil.
8) Other types of relays: such as optical relay, acoustic relay, thermal relay, instrument relay, Hall effect relay, differential relay, etc.
2. Classification according to overall dimensions of relay:
1) Miniature relay: the relay with the longest side size not greater than 10mm.
2) Subminiature miniature relay: relay with the longest side size greater than 10mm but not greater than 25mm.
3) Small miniature relay: relay with the longest side size greater than 25mm but not greater than 50mm.
Note: for sealed or enclosed relays, the overall dimension is the maximum dimension of the relay body in three mutually perpendicular directions, excluding the dimensions of mounting parts, leading out ends, pressing ribs, blank holders, flanging and sealing solder joints.
3. According to the load of relay, it is divided into:
1) Micro power relay: when the open circuit voltage of the contact is DC 28V, the (resistance) is 0.1A and 0.2A.
2) Low power relay: when the open circuit voltage of the contact is DC 28V, it is a relay with (resistance) of 0.5A and 1a.
3) Medium power relay: when the open circuit voltage of the contact is DC 28V, the (resistance) is 2a and 5A.
4) High power relay: when the open circuit voltage of the contact is DC 28V, the (resistance) is 10a, 15a, 20a, 25A, 40A... Relay.
4. Classification by relay protection characteristics:
1) Sealed relay: a relay with low leakage rate by sealing the contact and coil in the cover and isolating them from the surrounding medium by welding or other methods.
2) Enclosed relay: a relay that uses a housing to seal (unsealed) contacts and coils for protection. [5]
3) Open relay: relay without protective cover to protect electric shock, coil, etc.
Electromagnetic relay and dry spring relay are the most commonly used relays in electronic manufacturing.
Editing and broadcasting of technical parameters of main relay products
â‘ Rated working voltage: refers to the voltage required by the coil when the relay works normally. Depending on the relay model, it can be AC voltage or DC voltage.
â‘¡ DC resistance: refers to the DC resistance of the coil in the relay, which can be measured by multimeter.
â‘¢ Pull in current: refers to the minimum current that the relay can produce pull in action. In normal use, the given current must be slightly greater than the pull-in current, so that the relay can work stably. Generally, the working voltage applied to the coil shall not exceed 1.5 times of the rated working voltage, otherwise a large current will be generated and the coil will be burned.
â‘£ Release current: refers to the maximum current that the relay generates release action. When the current in the pull in state of the relay decreases to a certain extent, the relay will return to the release state without power on, and the current at this time is far less than the pull in current.
⑤ Contact switching voltage and current: refers to the voltage and current allowed to be loaded by the relay. It determines that the relay can control the voltage and current, which can not be exceeded during use, otherwise it is easy to damage the contact of the relay.
Relay test
â‘ Measuring contact resistance: measure the resistance between normally closed contact and moving point with the resistance gear of multimeter, and the resistance value shall be 0; The resistance between the normally open contact and the moving point is infinite. Thus, it can be distinguished that it is a normally closed contact and that it is a normally open contact.
② Measuring coil resistance: use multimeter R × Measure the resistance of the relay coil in gear 10 to judge whether there is an open circuit in the coil.
â‘¢ Measure pull in voltage and current: input a group of voltage to the relay with adjustable regulated power supply and ammeter, and connect ammeter in series in the power supply circuit for monitoring. Slowly increase the power supply voltage. When you hear the sound of relay closing, record the closing voltage and current. For accuracy, you can try averaging multiple times.
â‘£ Measure the release voltage and current: it is also connected and tested as described above. When the relay is pulled in, gradually reduce the supply voltage. When the release sound of the relay is heard again, record the voltage and current at this time. You can also try many times to obtain the average release voltage and current. Generally, the release voltage of the relay is 10% ~ 50% of the pull-in voltage. If the release voltage is less than 1 / 10 of the pull-in voltage, it cannot be used normally, which will threaten the stability of the circuit and make the operation unreliable.
Symbolic representation
The relay coil is represented by a rectangular box symbol in the circuit. If the relay has two coils, draw two parallel rectangular boxes. At the same time, the text symbol "J" of the relay shall be marked in or next to the rectangular box. There are two representations of relay contacts: one is to draw them directly on one side of the rectangular frame, which is more intuitive. The other is to draw each contact into its own control circuit according to the needs of circuit connection. Usually, the same text symbols are marked next to the contact and coil of the same relay, and the contact group is numbered to show the difference.
There are three basic forms of relay contacts:
(1) When the dynamic closing type (normally open, H-type) coil is not energized, the two contacts are disconnected, and the two contacts are closed after energization. It is indicated by the phonetic prefix "H" of the word "he".
(2) When the dynamic break type (normally closed, D type) coil is not energized, the two contacts are closed, and the two contacts are disconnected after energization. It is represented by the phonetic prefix "d" of the word "Duan".
(3) The conversion type (Z type) is the contact group type. This contact group has three contacts in total, that is, the middle is a moving contact and one static contact at the top and bottom. When the coil is not energized, the moving contact is disconnected from one of the static contacts and closed with the other; After the coil is energized, the moving contact moves, so that the original disconnected is in the closed state and the original closed is in the disconnected state, so as to achieve the purpose of conversion. Such a contact group is called a transfer contact. It is represented by the phonetic prefix "Z" of the word "Zhuan".
FBelec is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the research, development, production and sales of relay products.
NINGBO FBELE ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD.
FBELE company was founded in 1997, is China's leading manufacturer of acoustic and other electronic components, we designs,manufactures, distributes high quality products in very competitive price, bestservice, timely delivery, small order acceptable, etc. Our products include piezo ceramic element, piezoelectric buzzer, magnetic buzzer,speakers, transducer, receiver, electret condenser microphone, magnetic contact. Piezoelectric alarm,ultrasonic sensor,PZT ceramics,etc.
- Following 0
- Followers 0
- Send Msg